Recommended Websites
Articles
distill
Description
Selected Articles
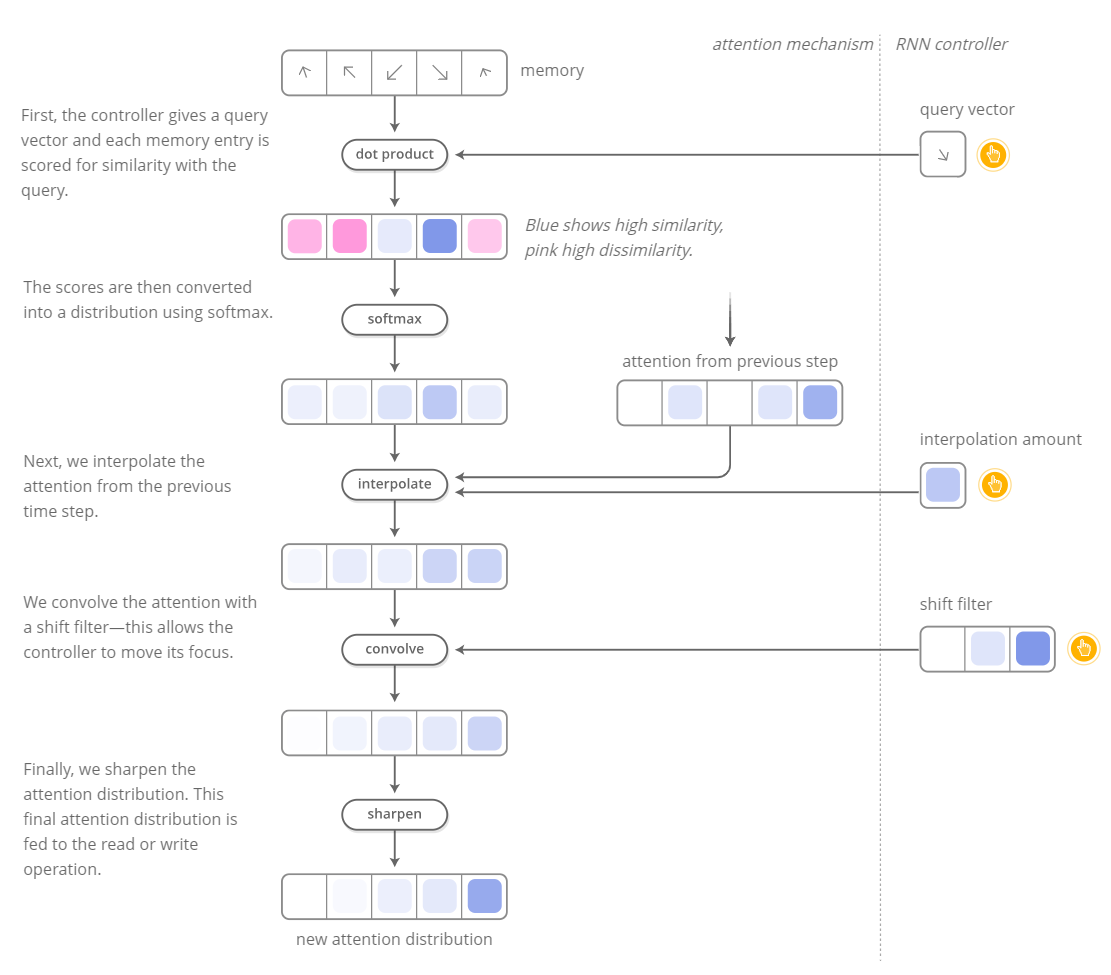
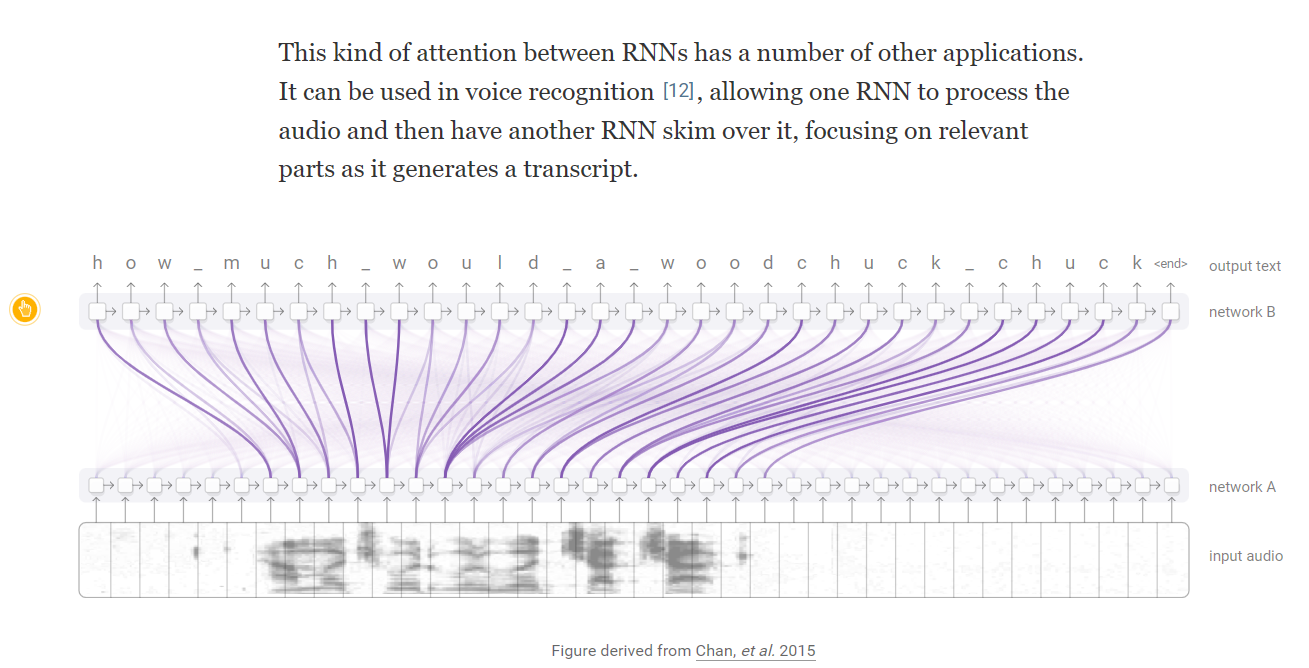
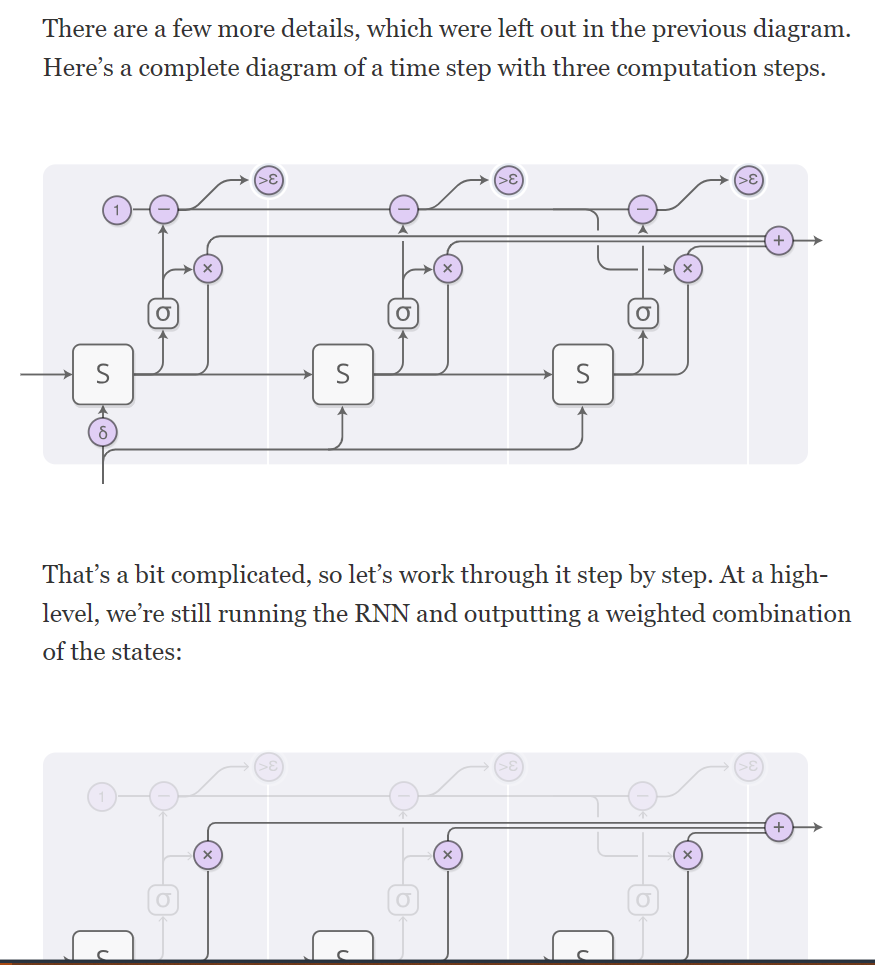
Attention and Augmented Recurrent Neural Networks
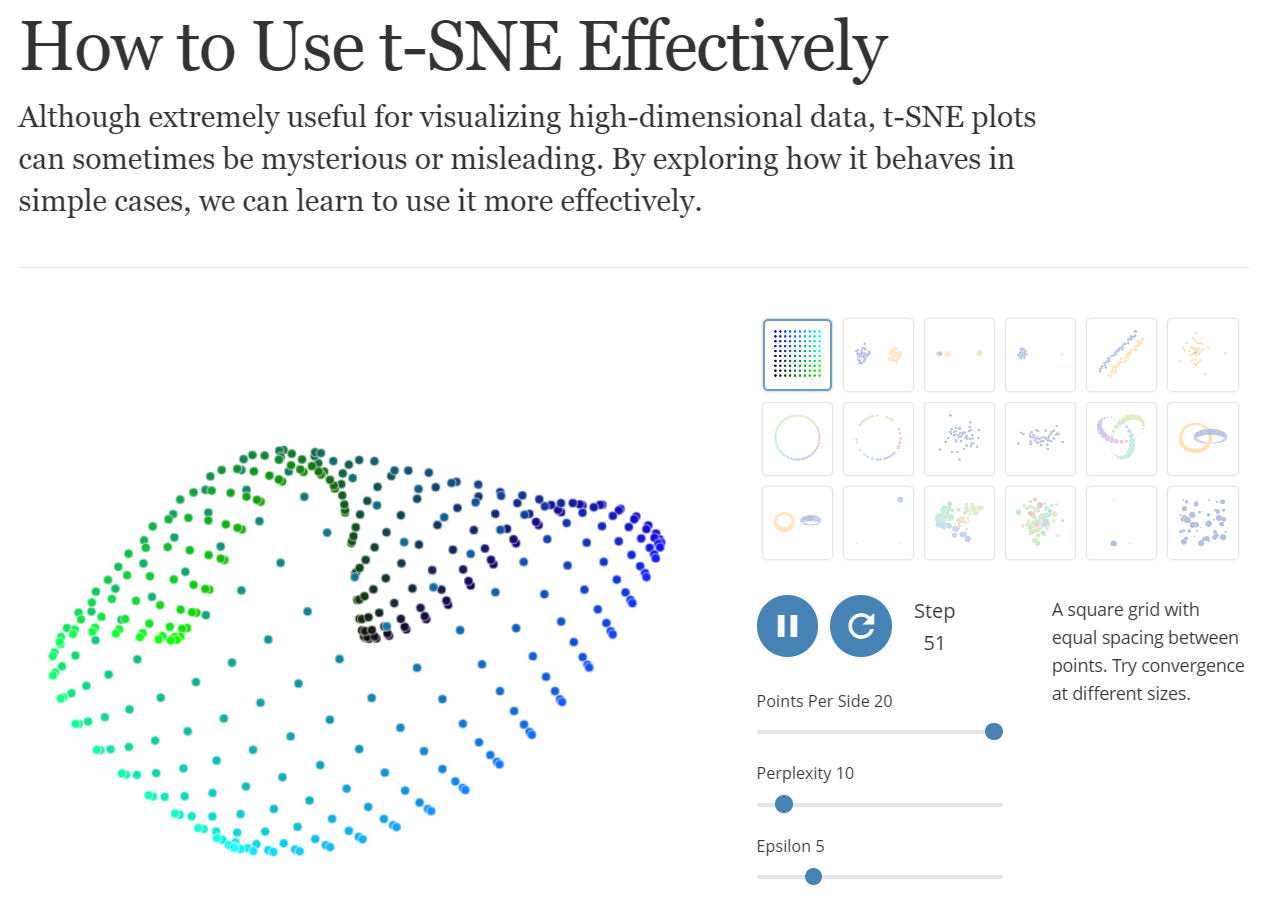
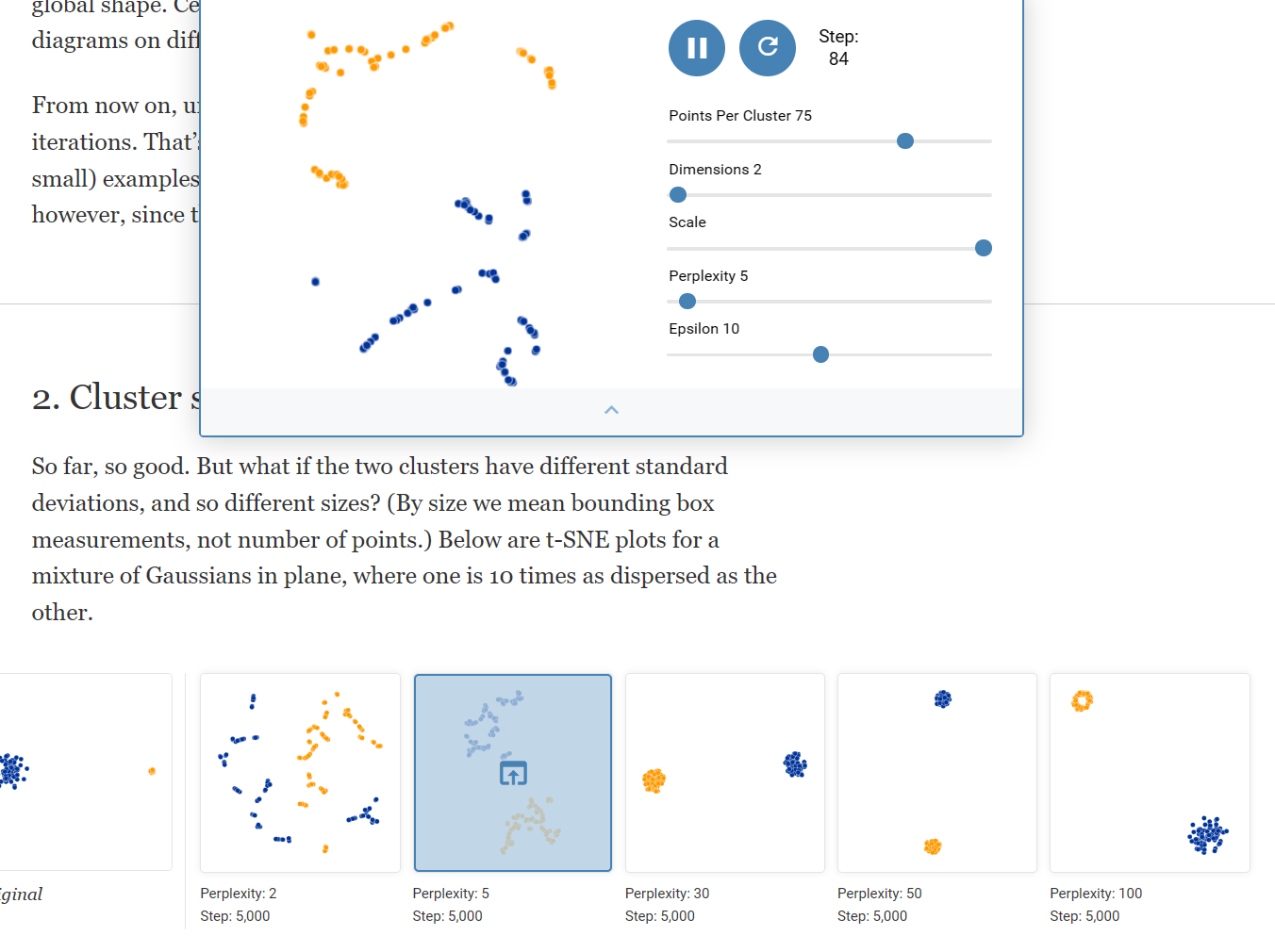
How to Use t-SNE Effectively
Although extremely useful for visualizing high-dimensional data, t-SNE plots can sometimes be mysterious or misleading. By exploring how it behaves in simple cases, we can learn to use it more effectively.
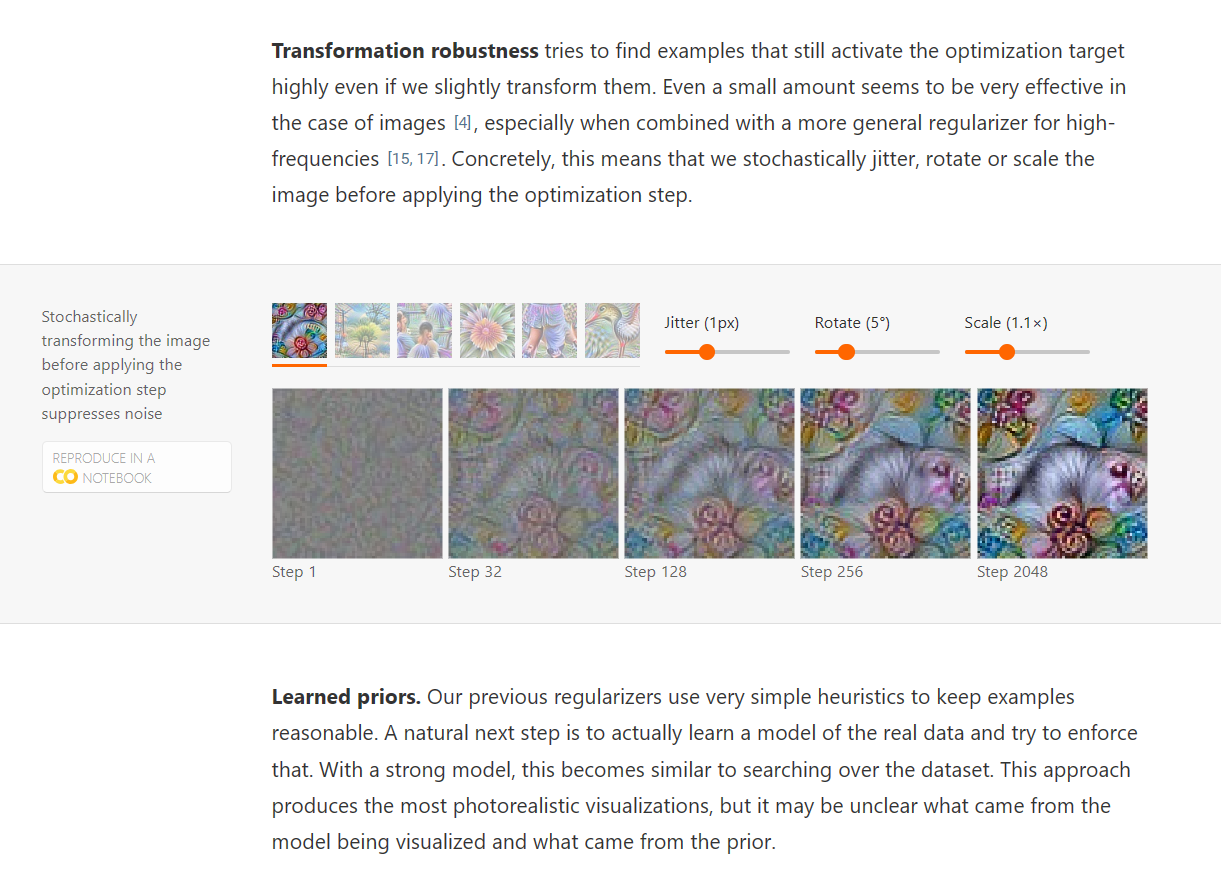
Feature Visualization
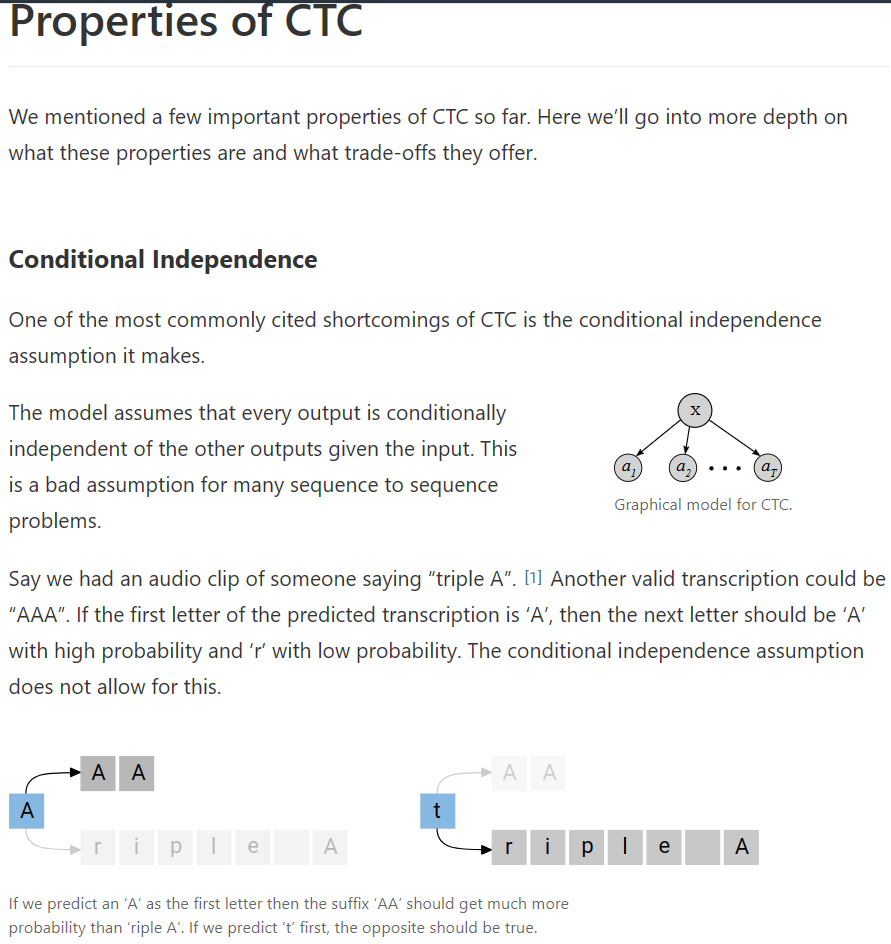
Sequence Modeling with CTC
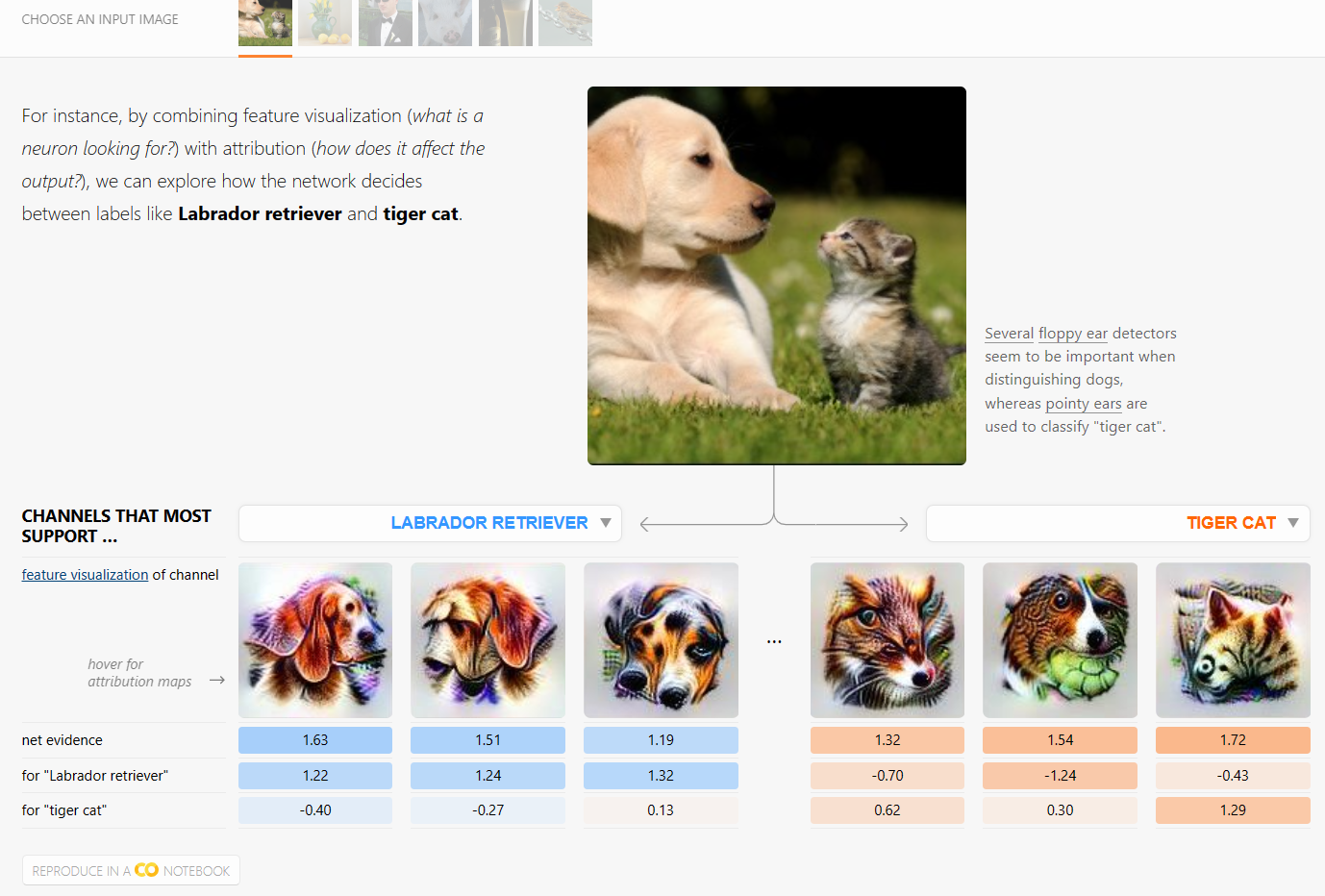
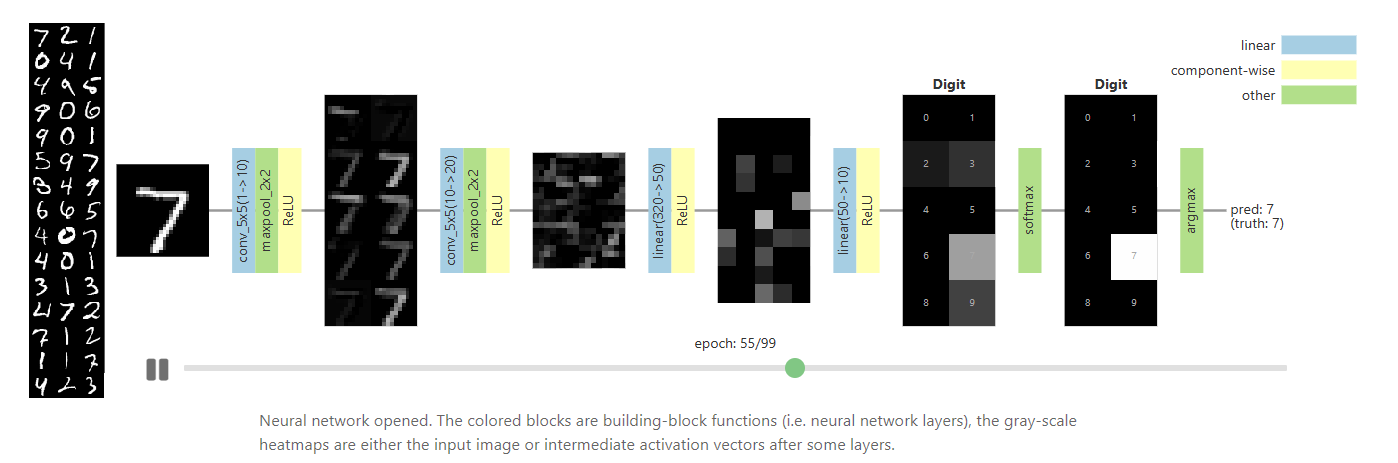
The Building Blocks of Interpretability
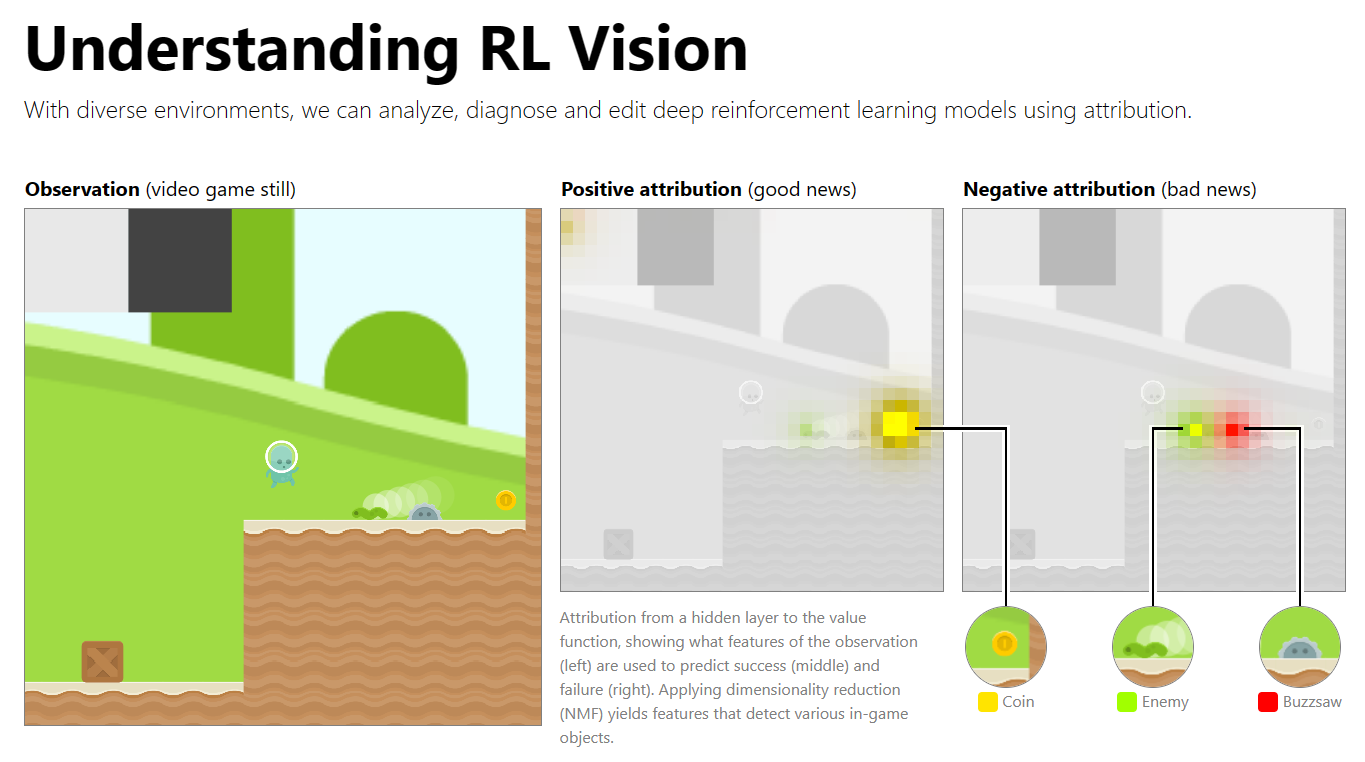
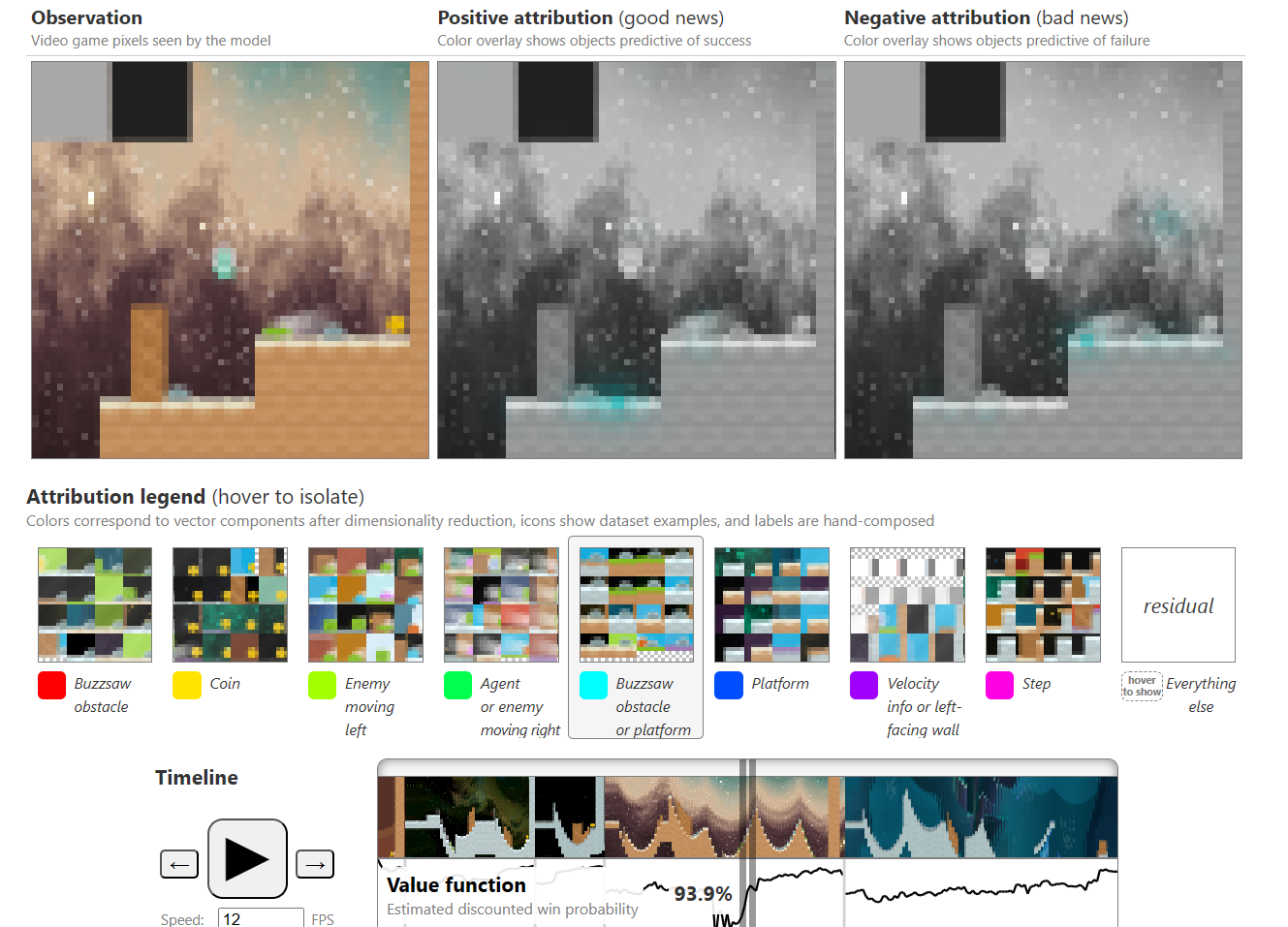
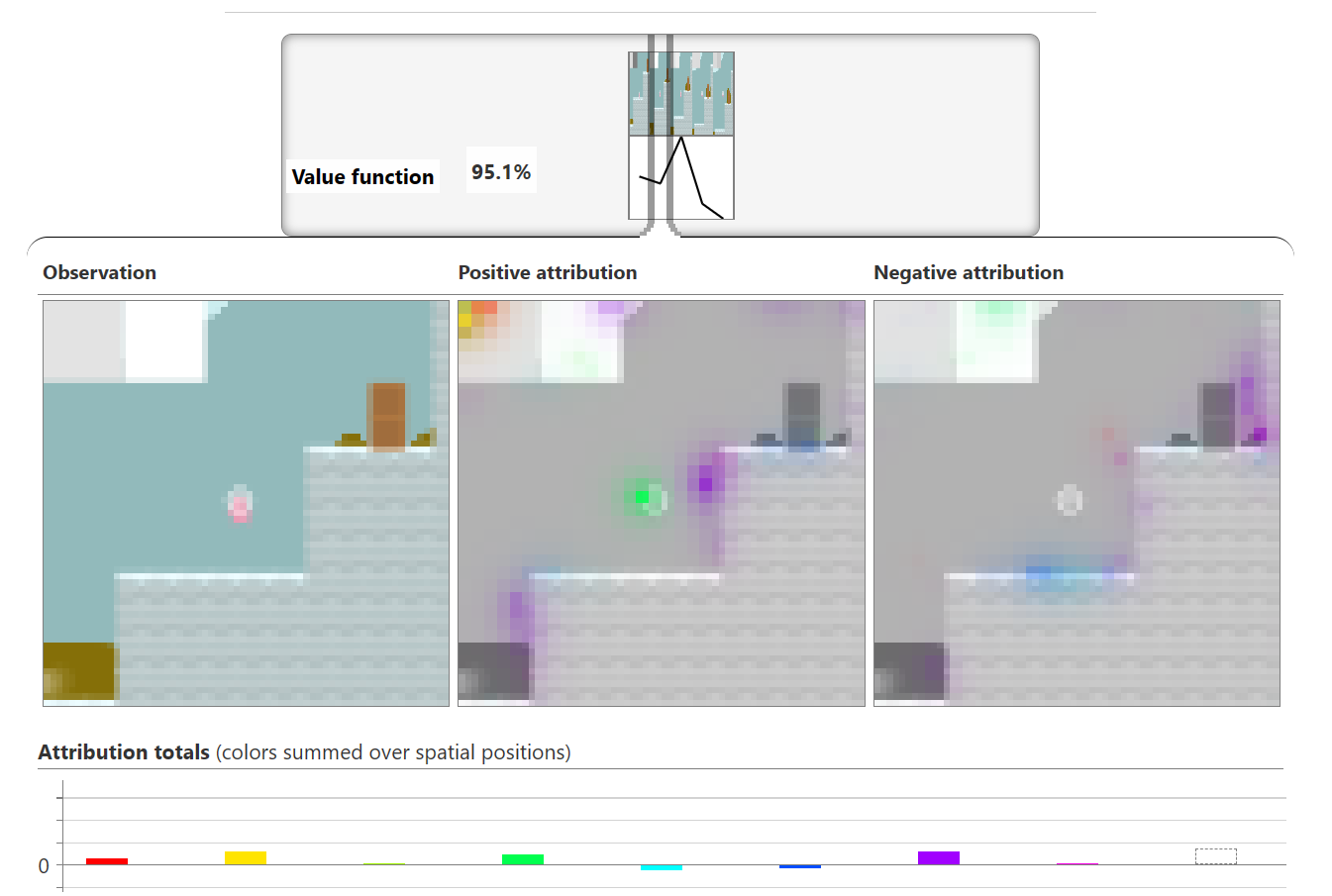
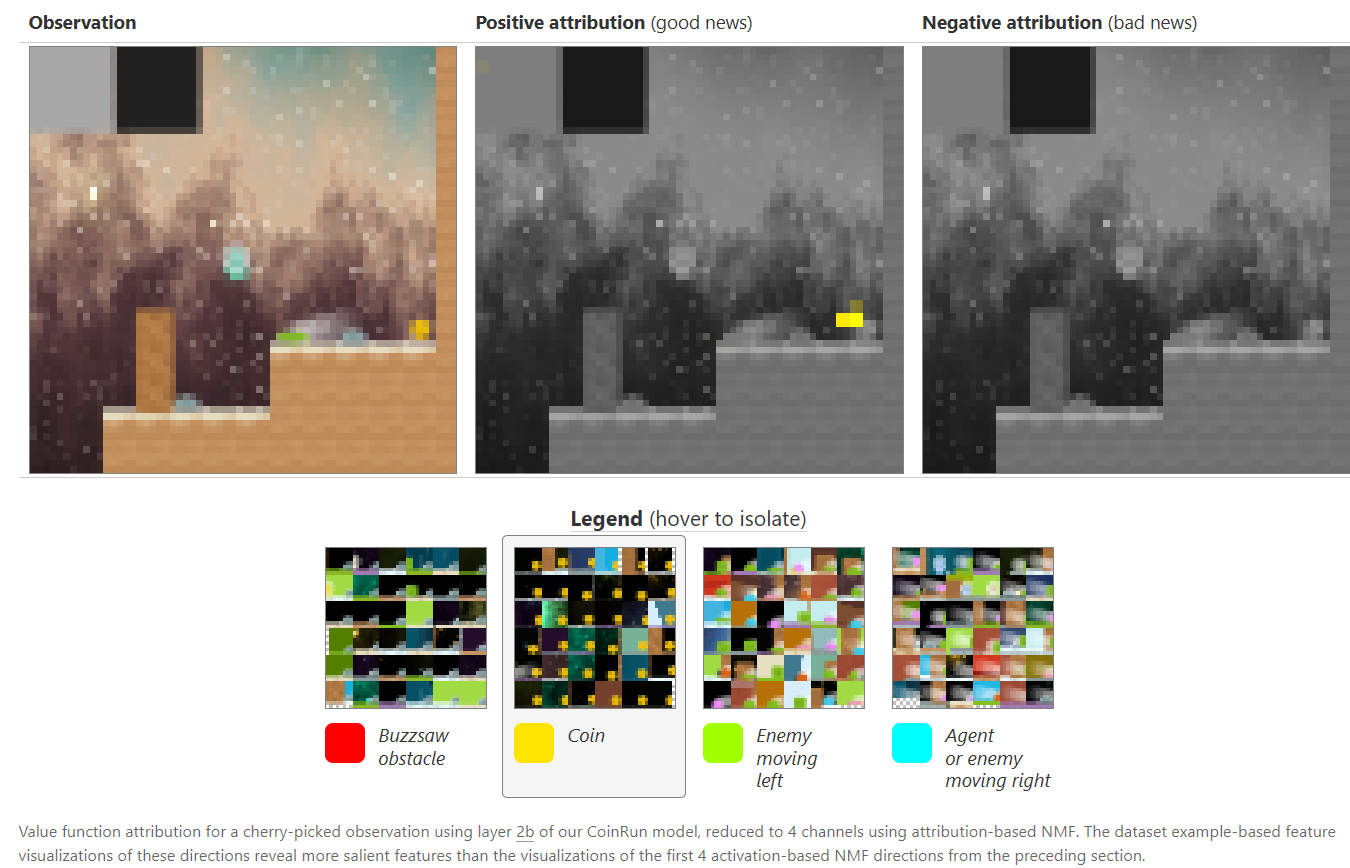
Interpretability techniques are normally studied in isolation. We explore the powerful interfaces that arise when you combine them — and the rich structure of this combinatorial space. For instance, by combining feature visualization (what is a neuron looking for?) with attribution (how does it affect the output?), we can explore how the network decides between labels like Labrador retriever and tiger cat.
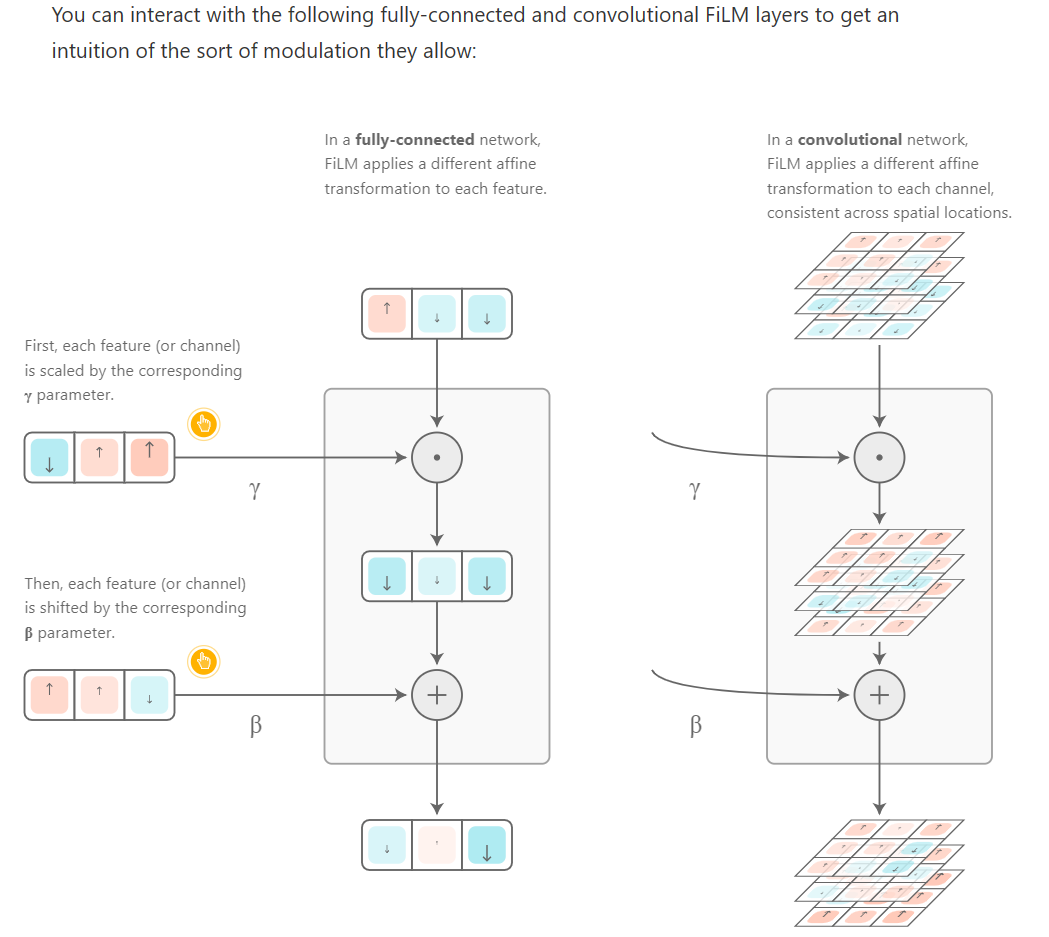
Feature-Wise Transformations
Many real-world problems require integrating multiple sources of information. Sometimes these problems involve multiple, distinct modalities of information — vision, language, audio, etc. — as is required to understand a scene in a movie or answer a question about an image. Other times, these problems involve multiple sources of the same kind of input, i.e. when summarizing several documents or drawing one image in the style of another.
Exploring Neural Networks with Activation Atlases
By using feature inversion to visualize millions of activations from an image classification network, we create an explorable activation atlas of features the network has learned which can reveal how the network typically represents some concepts.
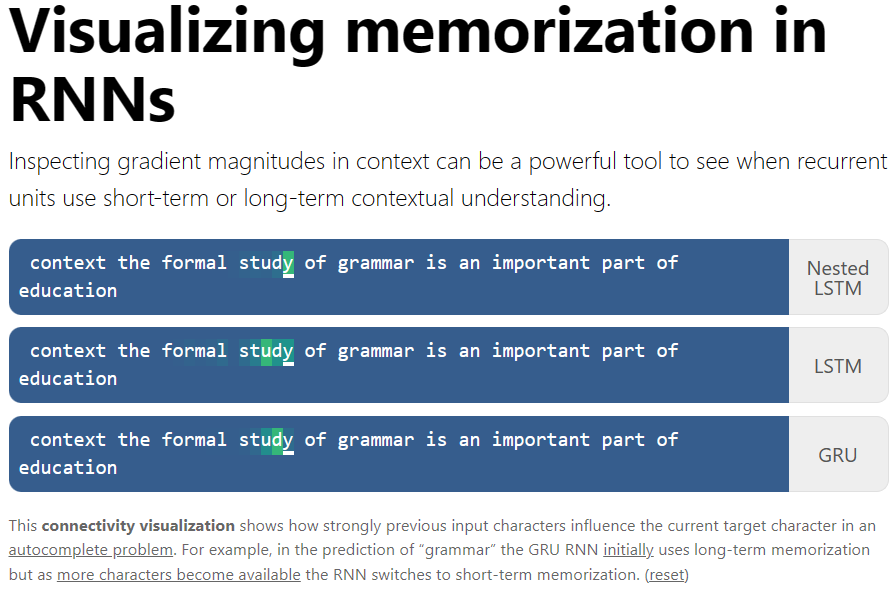
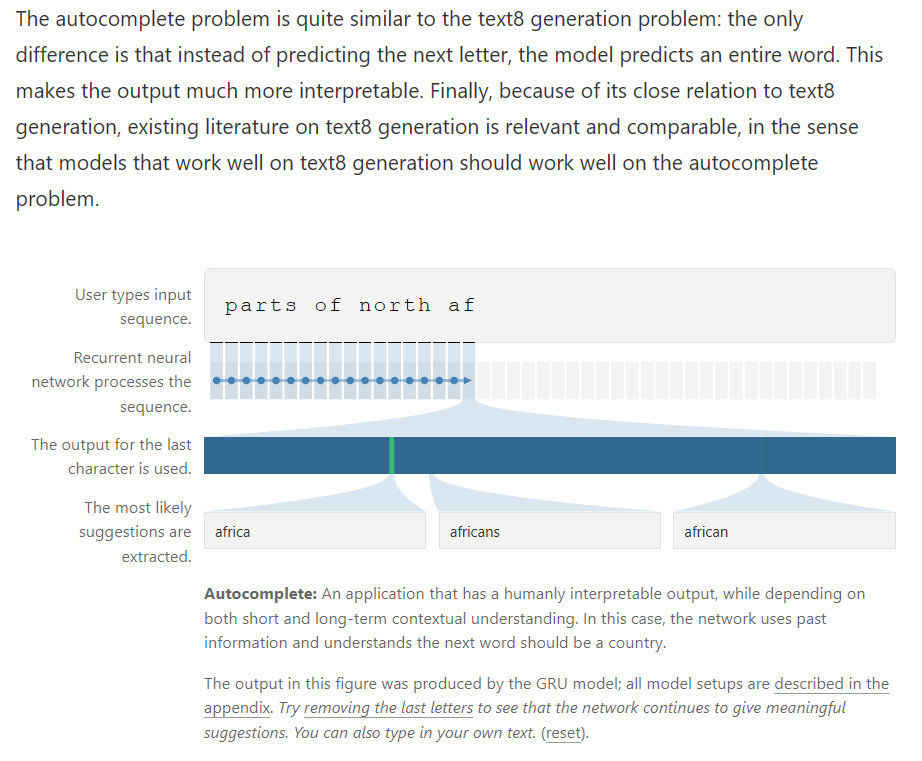
Visualizing memorization in RNNs
This article presents a qualitative visualization method for comparing recurrent units with regards to memorization and contextual understanding. The method is applied to the three recurrent units mentioned above: Nested LSTMs, LSTMs, and GRUs.
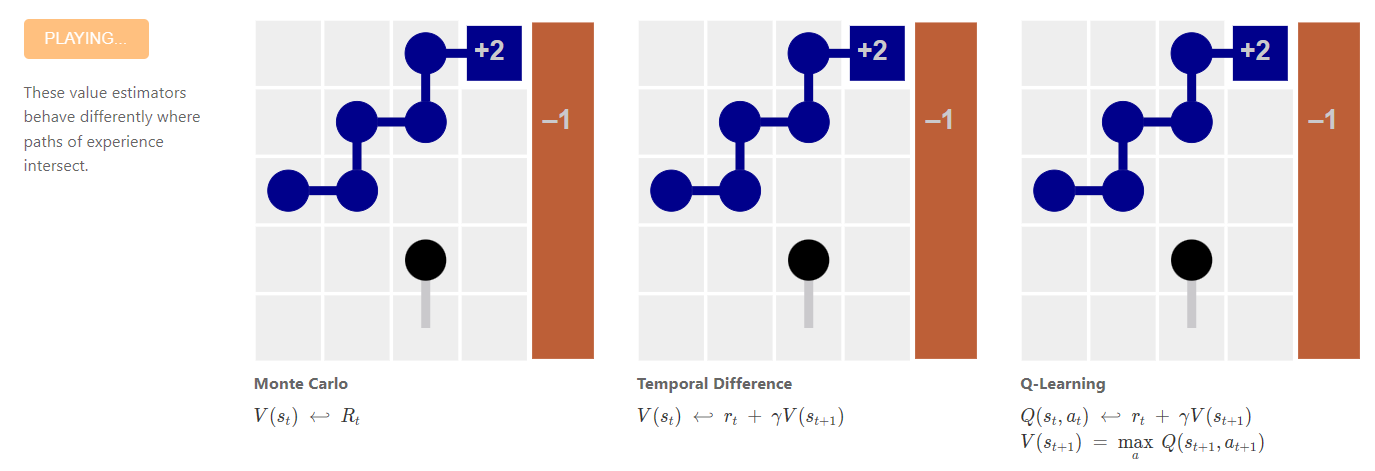
Paths Perspective on Value Learning
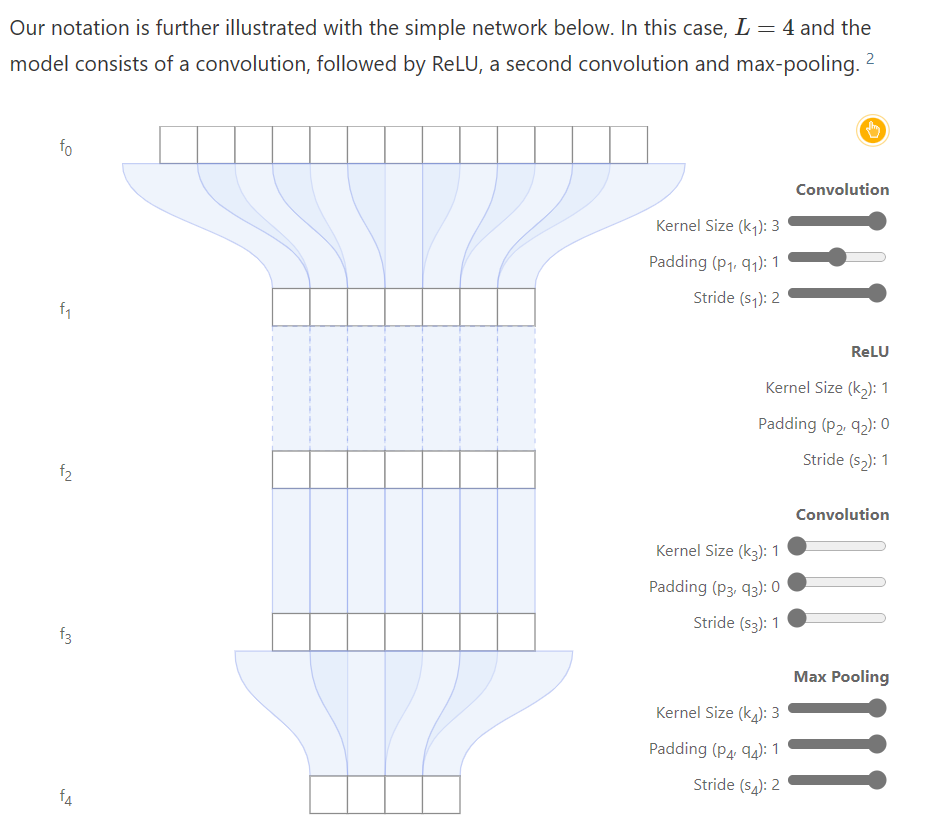
Computing Receptive Fields of Convolutional Neural Networks
<div class="infobox-row"><div class="infobox-head">Tagline</div><div class="infobox-spacer"></div><div class="infobox-tail">Mathematical derivations and <a href="https://github.com/google-research/receptive_field">open-source library</a> to compute receptive fields of convnets, enabling the mapping of extracted features to input signals.</div></div>
<div class="infobox-row"><div class="infobox-head">Link</div><div class="infobox-spacer"></div><div class="infobox-tail"><a href="https://distill.pub/2019/computing-receptive-fields/">https://distill.pub/2019/computing-receptive-fields/</a></div></div>
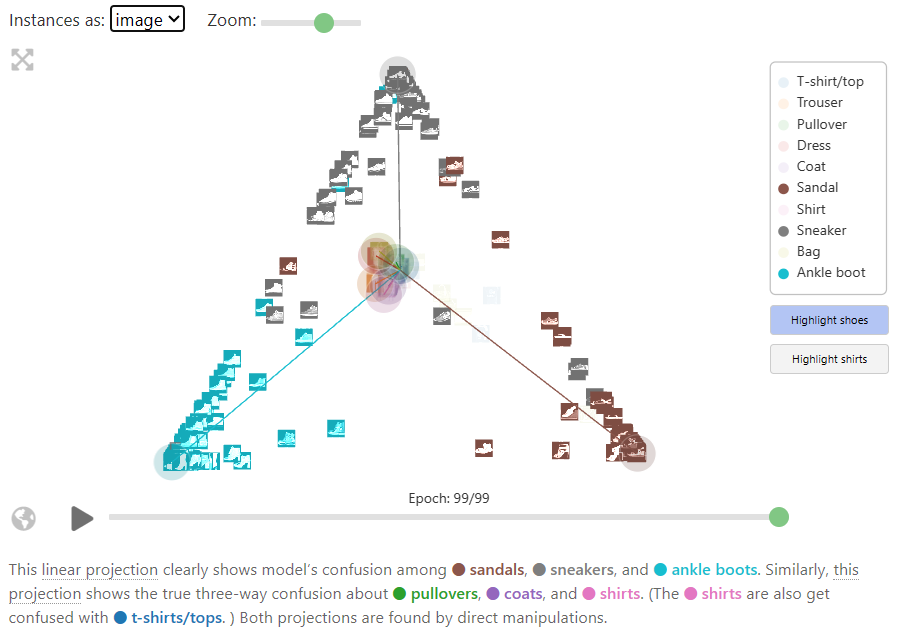
Visualizing Neural Networks with the Grand Tour
The Grand Tour is a classic visualization technique for high-dimensional point clouds that projects a high-dimensional dataset into two dimensions. Over time, the Grand Tour smoothly animates its projection so that every possible view of the dataset is (eventually) presented to the viewer. …
In this article, we show how to leverage the linearity of the Grand Tour to enable a number of capabilities that are uniquely useful to visualize the behavior of neural networks.
Concretely, we present three use cases of interest:
- visualizing the training process as the network weights change,
- visualizing the layer-to-layer behavior as the data goes through the network[,] and
- visualizing both how adversarial examples are crafted and how they fool a neural network.